Maple™ is the essential technical computing software for today's engineers,a mathematicians, and scientists. Whether you need to do quick calculations, develop design sheets, teach fundamental concepts, or produce sophisticated high-fidelity simulation models, Maple's world-leading computation engine offers the breadth, depth, and performance to handle every type of mathematics.
Maple technology has been trusted as a cutting edge mathematical and technical tool for over 25 years. In that time, millions of users from around the world have used and relied on the power of Maple for their research, testing , analysis, design, teaching, and schoolwork. Maple builds upon Maplesoft's rich product history in becoming the ultimate productivity mathematical problems and creating interactive technical documents.
The table shows the previous and the current Maple products:
| Product | Year released |
| Maple 6 | 2000 |
| Maple 7 | 2001 |
| Maple 8 | 2002 |
| Maple 9 | 2003 |
| Maple 9.5 | 2004 |
| Maple 10 | 2005 |
| Maple 11 | 2007 |
| Maple 12 | 2008 |
| Maple 13 | 2009 |
| Maple 14 | 2010(current) |











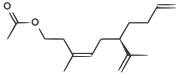
![(2S,5R)-2-ethyl-1,6-dioxaspiro[4.4]nonane](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8e/2S%2C5R-chalcogran-skeletal.svg/130px-2S%2C5R-chalcogran-skeletal.svg.png)




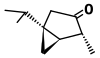
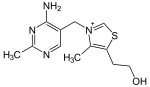






.gif)


